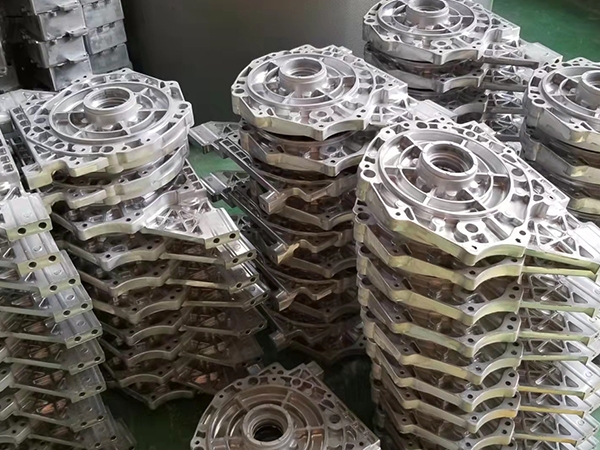
Low pressure cast aluminum series
-
Low pressure cast aluminum series
-
Sand cast aluminum parts series
-
Die cast aluminum parts series
-
Mechanical processing series
-
Sand casting aluminum series
-
Gravity Casting Series
-
Sand cast aluminum parts series
-
Die cast aluminum parts series
-
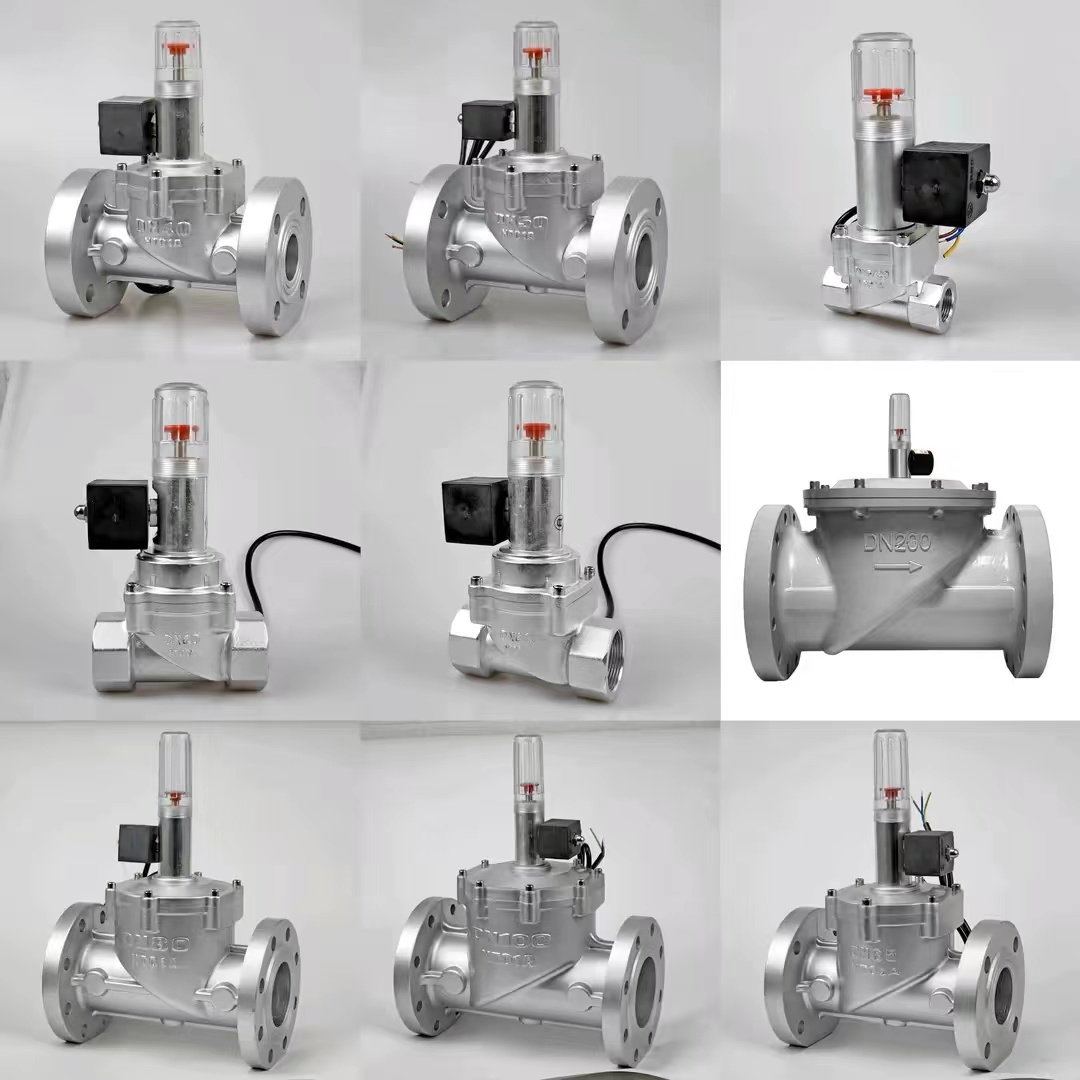
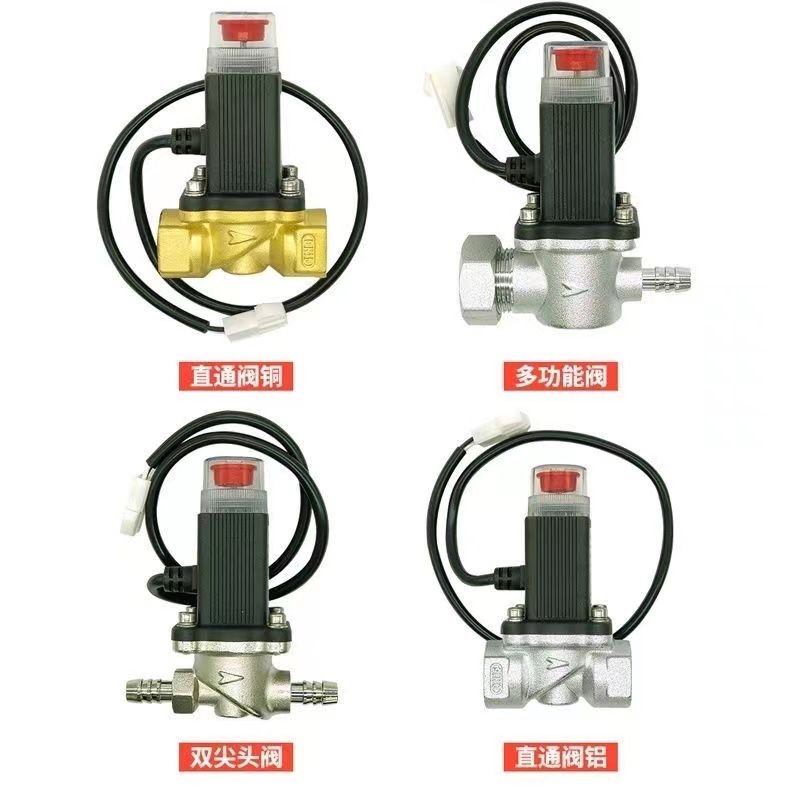
Electromagnetic gas emergency shut-off valve
-
Domestic gas emergency shut-off valve gas leakage
Hot Product
News
2024-05-12
2024-05-12
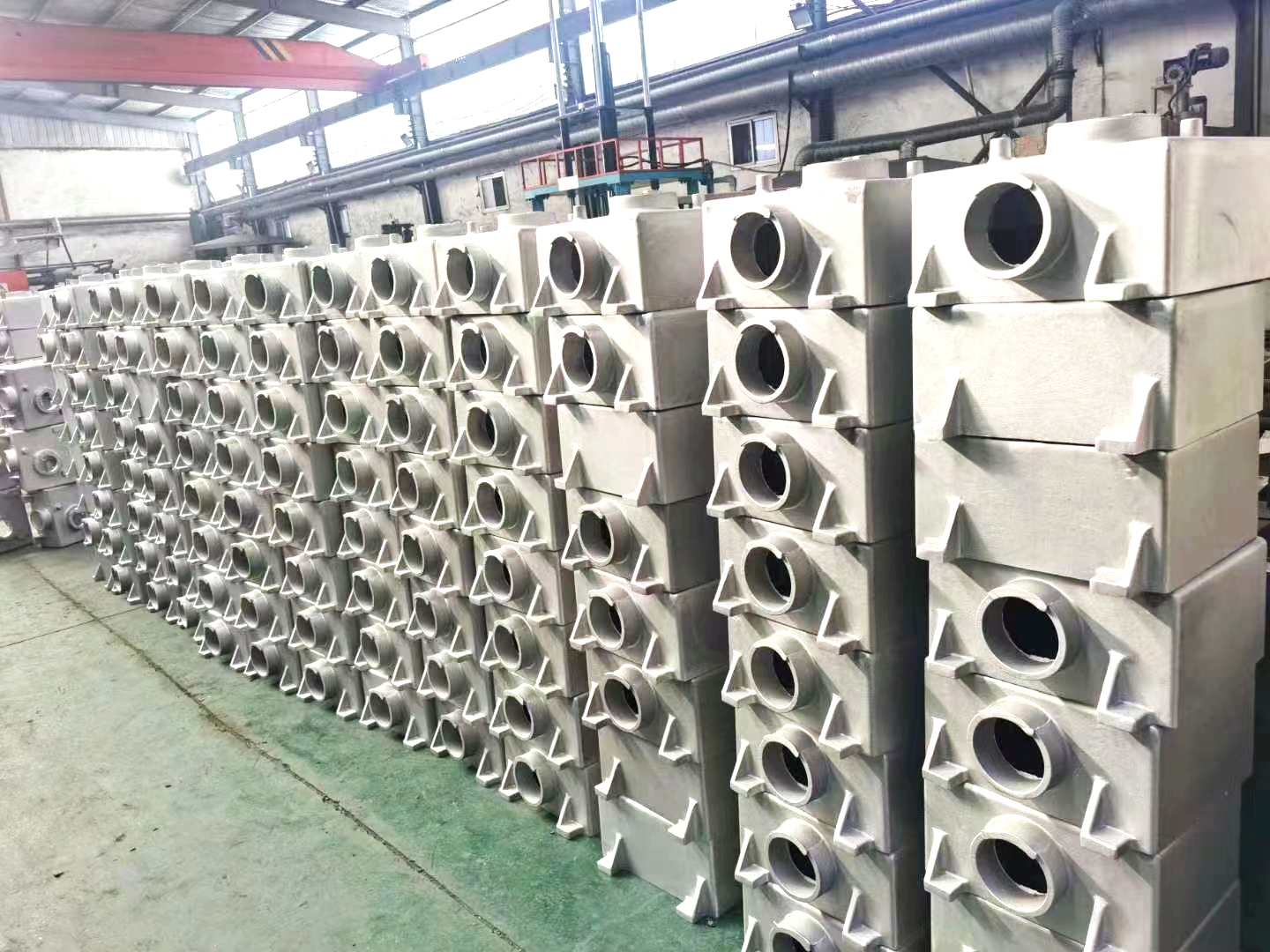
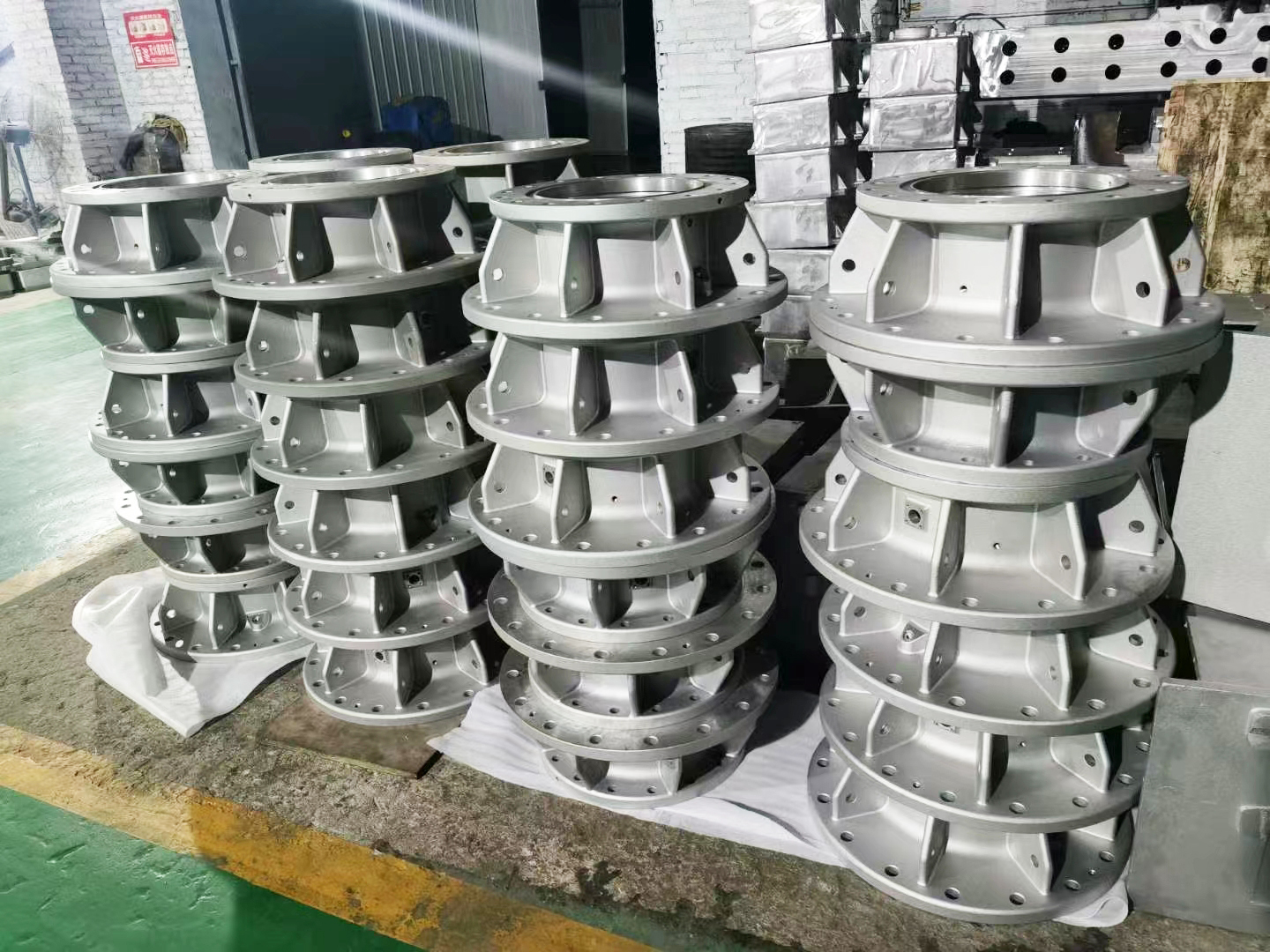
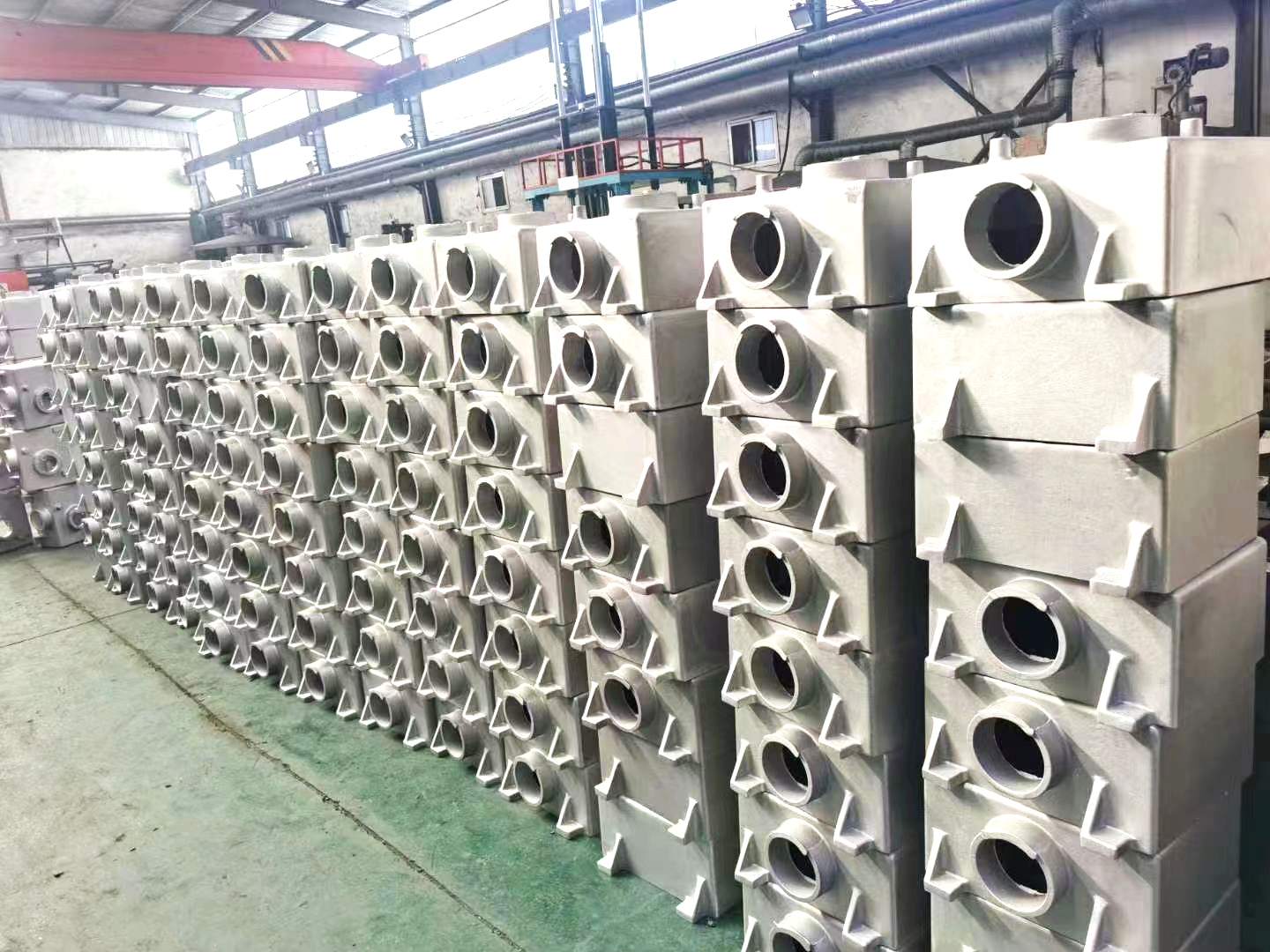



Low pressure casting manufacturer - Botou Quanle Metal Products Co., Ltd
Low pressure casting refers to a casting method in which the mold is generally placed above a sealed crucible, and compressed air is introduced into the crucible to create low pressure (0.06-0.15 MPa) on the surface of the molten metal, causing the metal liquid to rise from the riser to fill the mold and control solidification. This casting method has good shrinkage and dense casting structure, making it easy to cast large and complex thin-walled castings without the need for a riser. The metal yield reaches 95%. No pollution, easy to achieve automation. But the equipment cost is high and the production efficiency is low. Generally used for casting non-ferrous alloys.
principle
Low pressure casting is a casting method that presses liquid alloys into the mold cavity from bottom to top under pressure, and solidifies under pressure to obtain castings. The principle of low-pressure casting is shown in Figure 1 "Principle of Low Pressure Casting". Dry compressed air or inert gas is introduced into the sealed crucible, and with the help of the pressure acting on the metal liquid surface, the metal liquid is smoothly filled into the mold from bottom to top through the sprue along the riser, with a filling pressure of generally 20-60kPa. After the casting is completely solidified, release the gas pressure on the liquid surface to allow the non solidified metal liquid in the riser and runner to flow into the crucible by its own weight, then open the mold and remove the casting.
The low-pressure casting production process includes the following four basic processes:
1) Preparation of metal smelting and molds or molds.
2) Preparation before pouring: including sealing the crucible (assembly of sealing cover), scraping slag in the riser, measuring the liquid level height, sealing test, mold matching, tightening the mold or casting, etc.
3) Pouring: including liquid lifting, mold filling, pressurization, solidification, depressurization, and cooling.
4) Demolding: including loose mold demolding and removal of castings.